[About MultiBind]
[Server Help]
[Download]
Recognizes Spatial Chemical Binding Patterns Common to a Set of Protein Structures
| |
|
 |
[Home] [About MultiBind] [Server Help] [Download] |
| Multiple Alignment of Protein Binding Sites Recognizes Spatial Chemical Binding Patterns Common to a Set of Protein Structures |



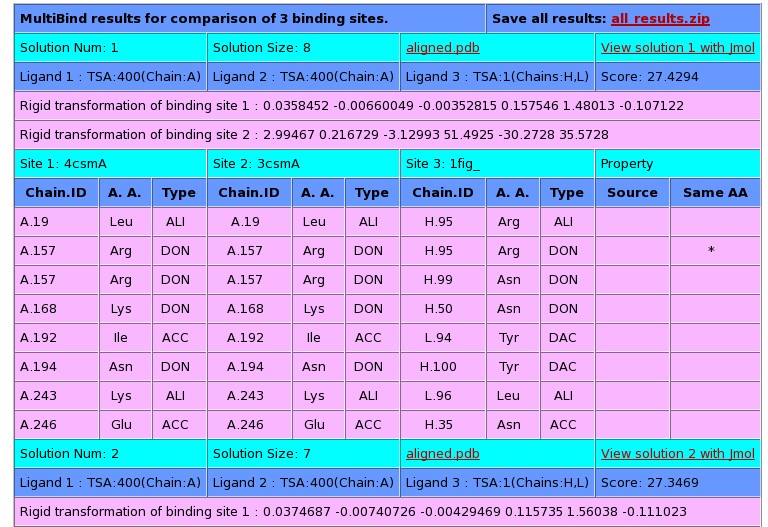
The 5 top ranking solutions are presented. Each solution can be
viewed with Jmol by clicking on the "View solution with Jmol". In
addition the PDB file with the superimposition of all the complexes
can be downloaded as a separated file (aligned.pdb).
The details of the following column fields can be found below
(click to jump to a description):
Chain.ID
AminoAcid
Property
Source
Dist
Conserved AA
Chain.ID:
The protein chain, followed by the
identity of the amino acid
AminoAcid:
The one
letter amino acid code. However it must be noted that the method is
based on the physico-chemical properties and does not consider the
identity of the amino acids. These are only displayed for the
convenience of analysis.
Property:
The
physico-chemical property that is matched by the algorithm. The method
is based on a representation of each amino acid of a protein as a set
of features that are important for its interaction with other
molecules. The abbreviations of these features are:
DON - Hydrogen bond donor
ACC - Hydrogen bond acceptor
DAC - Hydrogen bond donor and
acceptor (e.g in histidine)
ALI - Aliphatic Hydrophobic property
PII - Aromatic property (pi
contacts)
Source:
This field specifies whether the matched
property is contributed by the backbone or the side-chain of the amino
acid.
The abbreviations are:
b - feature contributed by the backbone
s - feature contributed by the
backbone
Dist:
The distance in space measured
between the matched features.
Conserved
AA:
Marks the features shared by the two molecules that are
contributed by residues with the same identity of the amino acid.
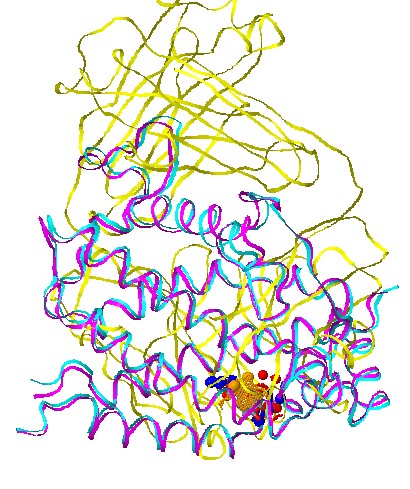
Stage 5 - Jmol options:
Each solution
can be visualized with Jmol. The default view presents the
superimposition of all the complexes, with their corresponding ligands
and the matched physico-chemical properties. The molecules are colored
by model (according to the order of input molecules, the first is
cyan, the second is magenta, the third is yellow). The
physico-chemical properties (pseudocenters) are represented as
balls. Hydrogen bond donors are blue, acceptors - red,
donors/acceptors - green, hydrophobic aliphatic - orange and aromatic
- gray. The surface points that have a similar location in all the
molecules are represented as smaller dots with the same coloring.
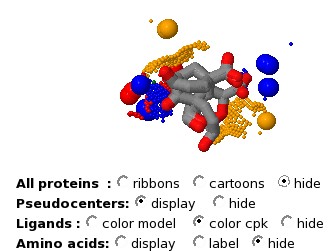
The "Radio groups" at the bottom allow to hide the protein molecules
and focus on the physico-chemical properties, the ligands or the amino
acids.
Please don't hesitate to contact if you have further problems or questions: shulmana@tau.ac.il
Reference: Shatsky M, Shulman-Peleg A, Nussinov R, Wolfson H.J. The Multiple Common Point Set Problem and its Application to Molecule Binding Pattern Detection, J. Comp. Biol., 2006, Vol 13, pp. 407-428.